2.9.2.3. Surrogate Modeling
Note
Surrogate modeling functionality of quoFEM is built upon GPy library (available under BSD 3-clause license), an opensource python framework for Gaussian process modeling developed in the Sheffield machine learning group.
The Train GP Surrogate Model module is used to construct a Gaussian process (GP) based surrogate model that substitutes expensive computational simulation models or physical experiments. Consider a simulation model, with input random variables (or parameters) \(\boldsymbol{x}\) and output quantity of interests, denoted as \(\boldsymbol{y}=f(\boldsymbol{x})\). A surrogate model for the corresponding simulation model can be built by different user-provided information types:
RV (model input \(\boldsymbol{x}\)) |
QoI (model response \(\boldsymbol{y}\)) |
|
|---|---|---|
Case1 |
bounds of random variables \(\boldsymbol{x}\) |
simulation model: \(\boldsymbol{y}=f(\boldsymbol{x})\) |
Case2 |
dataset: \(\{\boldsymbol{x^{(1)},x^{(2)}, ... ,x^{(N)}}\}\) |
simulation model: \(\boldsymbol{y}=f(\boldsymbol{x})\) |
Case3 |
dataset: \(\{\boldsymbol{x^{(1)},x^{(2)}, ... ,x^{(N)}}\}\) |
dataset: \(\{\boldsymbol{y^{(1)},y^{(2)}, ... ,y^{(N)}}\}\) |
Case 1 (Sampling and Simulation): User provides lower and upper bounds of each random variable (RV) and a simulation model. quoFEM will find the best training points sequentially by the adaptive design of experiments strategies until the model converges or reaches a user-specified computational tolerance.
Case 2 (Import RV Dataset and run Simulation): User provides sample population of RVs as a separate text file. quoFEM will run simulations to get QoI values and build a surrogate model.
Case 3 (Import both RV and QoI Dataset): User provides sample population of RVs and QoIs. quoFEM will not run any simulations and build a surrogate model purely based on the provided dataset.
Sampling (Adaptive DoE) |
Model simulation |
Surrogate Construction |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Case1 |
O |
O |
O |
Case2 |
X |
O |
O |
Case3 |
X |
X |
O |
The trained surrogate model can be saved in a file (.pkl format) along with a meta-information (.json format) and later imported in quoFEM in place of the original simulation model for UQ analysis or optimization purposes. See 2.2.5 for how to import the surrogate model in quoFEM.
Input description
Case 1: Sampling and Simulation
When the Training Dataset option is set to the Sampling and Simulation, a simulation model should be presented in the FEM tab. The training points are sampled adaptively by the design of experiments.
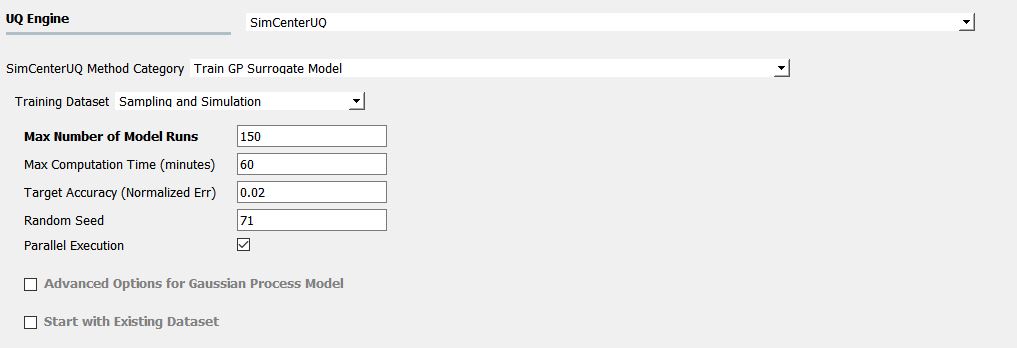
Fig. 2.9.2.3.1 Input panel for surrogate modeling
Maximum Number of Model Runs: When the number of simulation runs reaches the limit, the analysis will be terminated.
Maximum Computation Time (in minutes): When the tolerance limit of the computation time is reached, the analysis will be terminated. There will be a few minutes of error.
Target Accuracy (Normalized Error): The target accuracy is defined in terms of normalized root-mean squared error (NRMSE) estimated by leave-out-one cross-validation (LOOCV).
(2.9.2.3.3)\[\begin{align*} \rm{NRMSE} ~ &= \frac{\sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum^{N}_{k=1} (y_k-\hat{y}_k)^2}}{\max_{k=1,...,N}(y_k)-\min_{k=1,...,N}(y_k)} \end{align*}\]where\(y_k\) : exact response from the model simulation\(\hat{y}_k\): estimated response by LOOCV surrogate model prediction\(N\): number of samples used to train the surrogate modelRandom Seed: Seed of the random number generator
Parallel excution: This engine implemented multiprocessing (local) or mpi4py (remote) python packages to run parallel execution.
Note that the results from the parallel and serial run may not be exactly the same because parallel execution sets the number of batch DoE in order to maximize the use of resources (Default DoE interval: 5)
User can also activate the Advanced Options for Gaussian Process Model
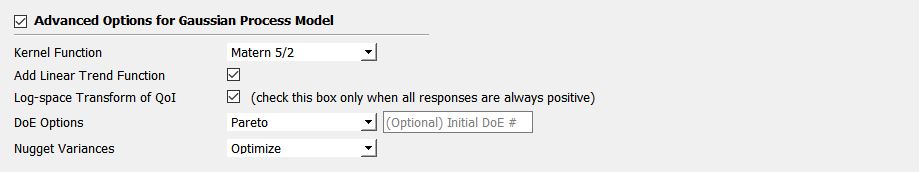
Fig. 2.9.2.3.2 Sampling and Simulation - Case 1
Kernel function: Correlation function for Gaussian process regression. Matern5/2 function is the default, and Matern3/2, Radial Basis, and Exponential functions are additionally supported.
Add Linear Trend Function: When increasing or decreasing trend is expected over the variables domain, a linear trend function may be introduced. The default is unchecked, ie. no trend function.
Log-space Transform of QoI: When the user can guarantee that the response quantities are always greater than 0, user may want to introduce a surrogate model in log-transformed space of QoI. The default is unchecked, ie. original physical coordinate.
Design of Experiments options: User may select the Adaptive DoE method and the number of the initial design of experiments (DoE) manually. The default is “none” and the default number of DoE is 4 times the number of random variables.
Nugget Variances: User may define nugget variances or bounds of the nugget variances if needed. The default is “optimize”.
Additionally, users may populate the initial samples directly from data files by activating Start with Existing Dataset
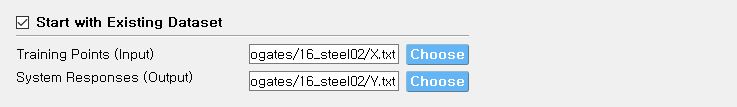
Fig. 2.9.2.3.3 Input panel for surrogate modeling
The following two data files are requested:
Train Points (Input)
System Responses (Output)
where
Each text file is a numeric table with the columns separated by a tab, space, or comma. Multiple headers can be presented following the symbol %.
The number of rows corresponds to the number of training data samples.
Train Points (Input): The number of columns should match the number of RVs presented in the RV tab and also match with required inputs of the simulation model provided in the FEM tab. The order of the columns should match thoses of the random variables presented in the RV tab (See Fig. 2.9.2.3.4 and Fig. 2.9.2.3.10 for example.)
System Responses (Output): The number of columns and the order of columns should match the QoI quantities presented in QoI tab.
Both files need to be provided, and the number of columns for the two files should be the same.
See Fig. 2.9.2.3.4 for example input data sheets.
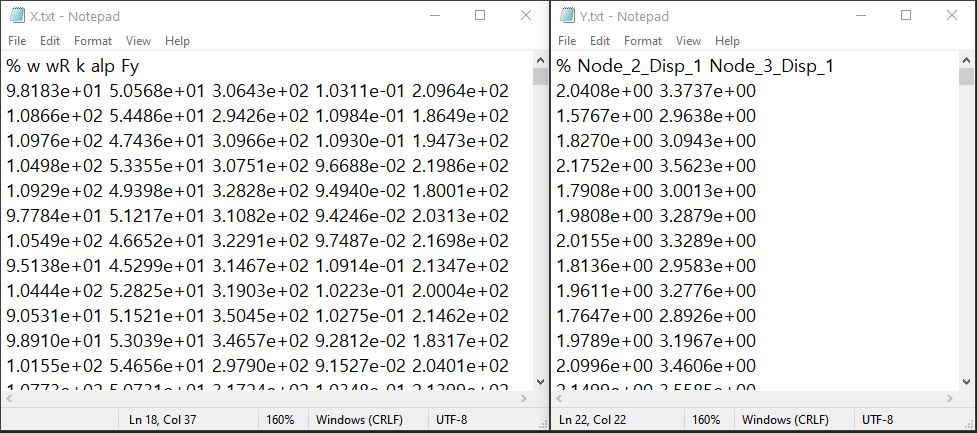
Fig. 2.9.2.3.4 Example of data input files
Note
When the Start with Existing Dataset is checked, one redundant simulation will be performed in order to check the consistency between the data and the simulation model. An error will be thrown when the dataset cannot be reproduced by the simulation model.
If the user wants to use the samples purely from data files and does not wish to introduce any simulation model, refer to Case 3 below.
Case 2: Import RV Dataset and run Simulation
When the Training Dataset option is set to Import Data File AND Get results from datafile check box is unchecked, quoFEM will run simulations to get result (QoI) values for imported RV locations and build a surrogate model.
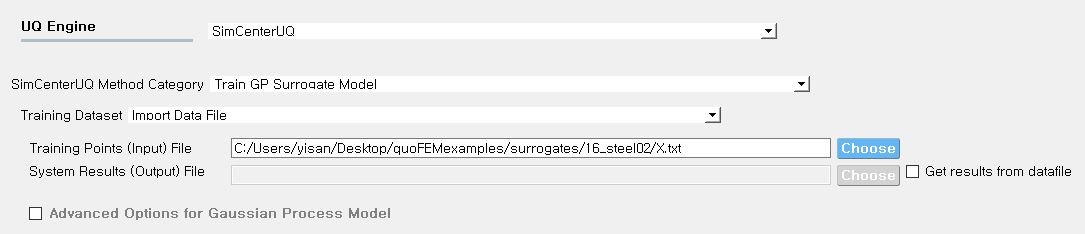
Fig. 2.9.2.3.5 Import Data File - Case 2
The following data file is requested
Train Points (Input)
where
The text file is a numeric table with columns separated by a tab, space, or comma. Multiple headers can be presented following the symbol %.
The number of rows corresponds to the number of training data samples.
The number of columns should match the number of RVs presented in the FEM model in the FEM tab. The order of columns should match those presented in the RV tab.
See Fig. 2.9.2.3.4 (left) for an example data file.
Case 3: Import both RV and QoI Dataset
When the Training Dataset option is set to Import Data File AND Get results from datafile check box is unchecked, quoFEM will not run any simulations and build a surrogate model purely based on the user-provided dataset.
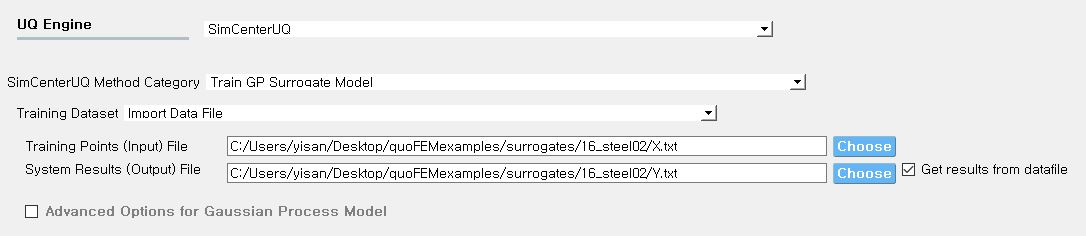
Fig. 2.9.2.3.6 Import Data File - Case 3
The following two data files are requested:
Train Points (Input)
System Responses (Output)
where
Each text file is a numeric table with columns separated by a tab, space, or comma. Multiple headers can be presented following the symbol %.
The number of columns corresponds to the number of training data samples.
The number of rows of each file respectively corresponds to the number of RVs and QoIs.
Both files need to be presented, and the number of columns should correspond to each other.
See Fig. 2.9.2.3.4 for example data files.
FEM tab will be inactivated in Case 3 as model information is not required.
Tip
Surrogate model training can be continued after termination by reusing RV and QoI samples obtained by the previous training.
Multi-Fidelity Modeling
When a user provides two different models, i.e. high and low fidelity models, the surrogate model for the high fidelity can be constructed with better performance in assisted by the low fidelity simulation results. The two models should share the same input RVs and output QoIs pools. Ideally, combined model should have the best prediction better than each individual ones, however, the benefit from low fidelity model differs depending on the correlation between the two model outputs [Patsialis2021]. Currently, adaptive design of experiments capacity of the multi-fidelity surrogate modeling is NOT supported.
Note
Multi-fidelity surrogate modeling functionality of quoFEM is built upon emukit library (available under Apache-2.0 license), an opensource python toolkit for emulation (surrogate modeling) and decision making under uncertainty.
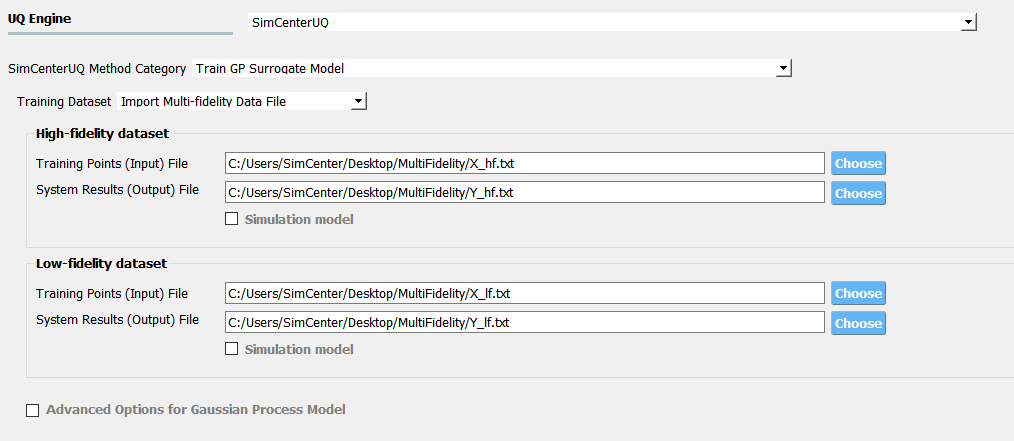
Fig. 2.9.2.3.7 Multi-fidelity modeling panel
For each fidelity models, either model, data, or both can be provided for each fidelity level.
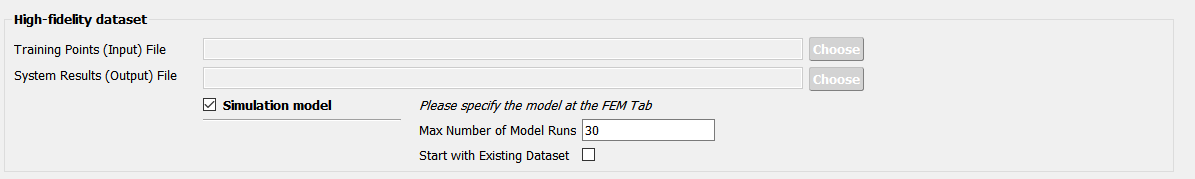
Fig. 2.9.2.3.8 Providing a simulation model for the high-fidelity response
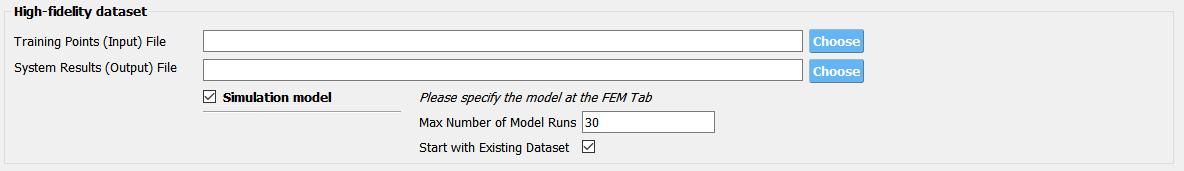
Fig. 2.9.2.3.9 Directly providing input(RV)-response(QoI) data pair of high-fidelity model
RV (Random Variables) Tab
Case 1 and 2: The bounds of RVs need to cover the domain of interest in future applications, while it should not be unnecessarily stretched. Input type and Distribution should be set to Parameters and Uniform. When dataset is provided, make sure to match the order of RVs in the RV tab to the order of data columns. Any correlation values will be ignored.
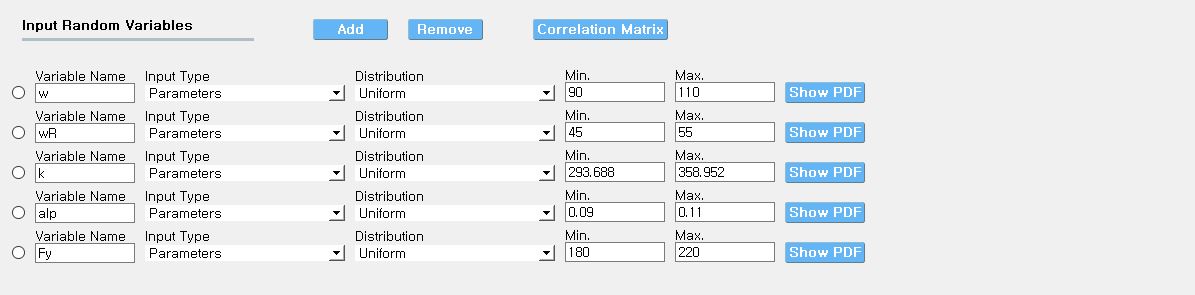
Fig. 2.9.2.3.10 Example of RV tab
Case 3: RV data tab will be populated automatically as soon as the dataset is imported.
Output description
Goodness-of-Fit
Once the training is completed, the following three verification measures are presented based on leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV) error estimation.
Leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV)
LOOCV prediction \(\hat{\boldsymbol{y}}_k\) at each sample location \(\boldsymbol{x}_k\) is obatined by the following procedure: A temporary surrogate model \(\hat{\boldsymbol{y}}=f^{sur}_{loo,k}(\boldsymbol{\boldsymbol{x}})\) is constructed using the samples \(\{\boldsymbol{x}_1,\boldsymbol{x}_2,...,\boldsymbol{x}_{k-1},\boldsymbol{x}_{k+1},...,\boldsymbol{x}_N\}\) and the calibrated parameters, and the prediction \(\hat{\boldsymbol{y}}_k=f^{sur}_{loo,k}(\boldsymbol{x}_k)\) is compared with the exact outcome \(y_k=f(\boldsymbol{x}_k)\).R2 error
R2 error is defined in terms of the total sum of squares over the residual sum of squares(2.9.2.3.2)\[\begin{align*} R^2 &= 1 - \frac{\sum^N_{k=1} (\hat{y}_k-\mu_\hat{y})^2}{\sum^N_{k=1} (\hat{y}_k-y_k)^2} \end{align*}\]The surrogate model is considered well-trained when the R2 (<1) approaches 1Normalized root-mean-squared-error (NRMSE)
(2.9.2.3.3)\[\begin{align*} \rm{NRMSE} ~ &= \frac{\sqrt{\frac{1}{N_t} \sum^{N_t}_{k=1} (y_k-\hat{y}_k)^2}}{\max_{k=1,...,N_t}(y_k)-\min_{k=1,...,N_t}(y_k)} \end{align*}\]The surrogate model is considered well-trained when the NRMSE (>0) approaches 0Correlation coefficient
Correlation coefficient is a statistic that measures linear correlation between two variables(2.9.2.3.4)\[ \rho_{y,\hat{y}} = \frac{\sum^N_{k=1}(y_k-\mu_{y})(\hat{y}_k-\mu_{\hat{y}})} {\sigma_y \sigma_\hat{y}}\]where\(\mu_{y}\) : mean of \(\{y_k\}\)\(\mu_{\hat{y}}\): mean of \(\{\hat{y}_k\}\)\(\sigma_{y}\): standard deviation of \(\{y_k\}\)\(\sigma_{\hat{y}}\): standard deviation of \(\{\hat{y}_k\}\)The surrogate model is considered well-trained when the correlation coefficient ( \(-1<\rho<1\) ) approaches 1Additionally scatter plot between the predicted and exact responses are presented: Well-trained model will form a clear diagonal line while poorly trained model are more scattered around.
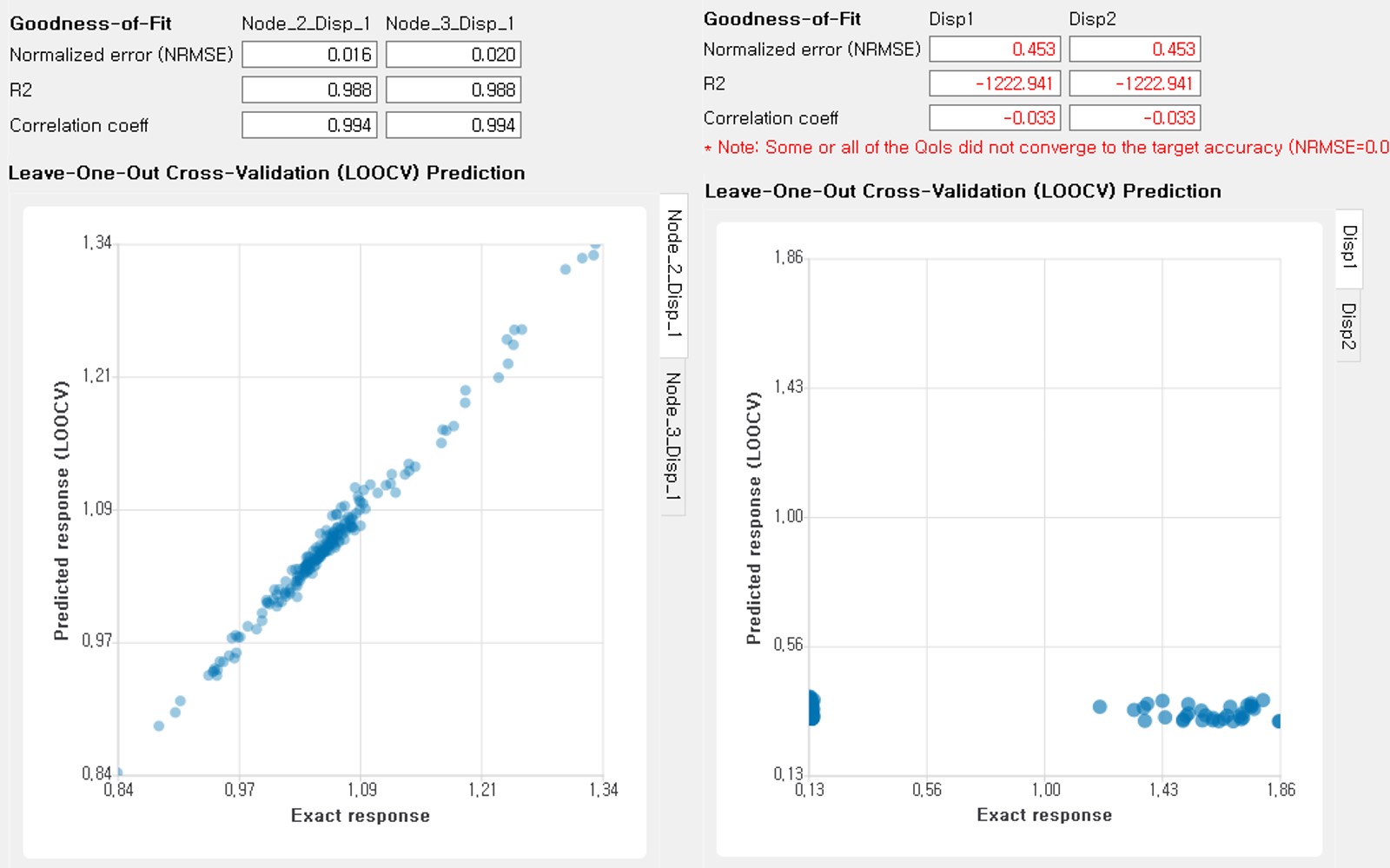
Fig. 2.9.2.3.11 Well-trained surrogate (left) and poorly trained surrogate (right) models
Note
Since these validation measures are calculated from the cross-validation predictions, they can be biased, particularly when highly localized nonlinear range exists in actual response surface and those regions are not covered by the training samples. The introduction of adaptive DoE helps to suppress the bias by enabling the targeted selection of simulation points around potentially faulty regions.
Warning
Note that GP-based surrogate models can be used to fit only smooth, continuous functions. When the surrogate model is poorly trained, a parametric study is highly recommended to check any possible discontinuity presented in the simulation model.
Saving Options
Save GP Model: The constructed surrogate model is saved. Two files and a folder will be saved, which are the SurroateGP Info File (default name:
SimGpModel.json), SurroateGP model file (default name:SimGpModel.pkl), and Simulation template directory that contains the simulation model information (templatedir_SIM). IMPORTANT: User may NOT change the name of the template directorytemplatedir_SIM.Save GP Info: This is a report generated for user reference. It contains the GP model parameter and other information. The default file name is
GPresults.out.RV Data, QoI Data:It saves the samples of RV and QoI. The default file names are
X.txtandY.txt, respectively. IMPORTANT: To continue surrogate modeling with additional simulations, save the RV and QoI sample files using this button and import them as initial points. Refer to the ‘Start with Existing Dataset’ option in Case 1.
Fig. 2.9.2.3.12 Saving options
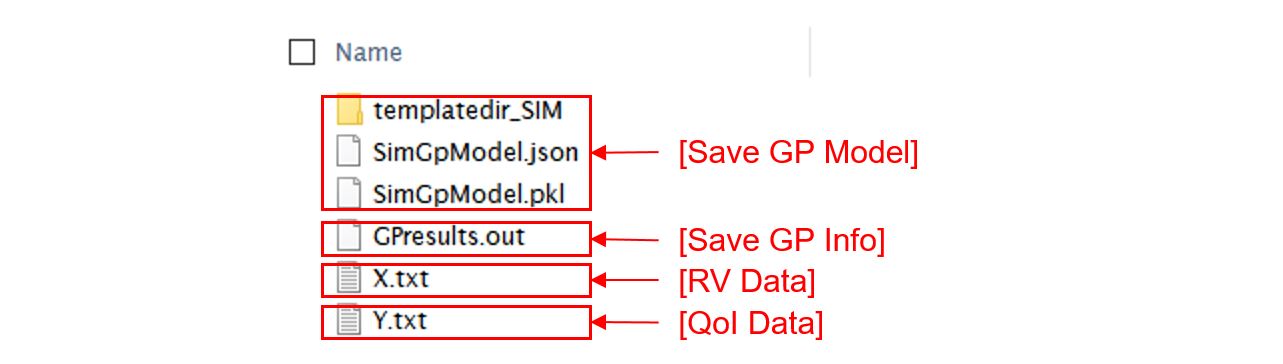
Fig. 2.9.2.3.13 Example outputs from saving options
- Patsialis2021
Patsialis, D., and A. A. Taflanidis. (2021). Multi-fidelity Monte Carlo for seismic risk assessment applications. Structural Safety 93: 102129.